Home [spacer] What is Process Automation?
What is Process Automation?
Definition: Business process automation is the execution of an end-to-end process, which includes individual steps accross multiple monolithic systems using workflows, artificial intelligence and RPA.

Benefits of Process Automation
- Increased efficiency: Automating processes reduces the amount of time and resources required to complete a task, increasing productivity and efficiency.
- Improved accuracy: Automation can help eliminate errors caused by human oversight or fatigue, ensuring that processes are completed accurately and consistently.
- Cost savings: By reducing the need for manual labor and improving accuracy, process automation can lead to significant cost savings for businesses.
- Better customer experience: Automated processes can help ensure that customers receive timely and consistent service, improving their overall experience with a company.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, automated processes can scale to handle larger volumes of work without the need for additional manpower.
Overall, process automation can help companies become more competitive, flexible and responsive to changing market conditions.
BPA vs. RPA
Business Process Automation (BPA) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) are both types of process automation technologies, but there are some key differences between them:
- Scope of automation: BPA is focused on automating entire business processes, while RPA is focused on automating specific tasks within a process.
- The complexity of automation: BPA is designed to handle complex business processes that may involve multiple systems, applications, and stakeholders. RPA, on the other hand, is typically used for simpler, more repetitive tasks.
- Level of human involvement: BPA may include some level of human involvement, such as approving a request or deciding based on a report. RPA is fully automated and does not require human involvement.
- Technology requirements: BPA requires more complex technology solutions, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems or business process management (BPM) software. RPA can be implemented using simpler, more lightweight software solutions.
- Implementation time: BPA initiatives can take longer to implement, as they require a more in-depth analysis of existing business processes and may involve significant changes to the organization's structure and workflows. RPA can often be applied relatively quickly, as it focuses on automating specific tasks within a process.
BPA and RPA are both valuable process automation technologies, but they are designed for different use cases. BPA is best suited for complex, end-to-end business processes, while RPA is better suited for automating specific, repetitive tasks within a process.
Success factors for implementing BPA
Here are some best practices for iPaaS that can help ensure successful implementation and adoption:
- A clear understanding of the existing processes as well as identifying areas that need improvement. This helps to avoid automating inefficient or redundant processes.
- Setting clear goals ensures that automation efforts are in line with the company's strategic objectives. In this way, priorities can be set for the processes to be automated and the right resources allocated.
- Selecting the right automation technology to meet the needs of the business. The technology should be flexible, scalable and able to integrate with existing systems and applications.
- Adequate training and support is essential to ensure that users can use the BPA system effectively. This minimizes errors and ensures that automation measures deliver the expected benefits.
- Continuous improvement ensures that the BPA system remains effective and adds value over time. This requires monitoring processes and identifying areas for improvement and optimization.
By following these best practices, organizations can maximize the benefits of iPaaS and ensure that their integrations are secure, scalable, and maintainable over time.
Process Automation through Scheer PAS
- Integration of all modern mechanisms for process automation, including artificial intelligence and software robots (Robotic Process Automation).
- Implementation of hyper-automation scenarios of any kind: Deployment services of automation solutions can be used directly in the platform through artificial intelligence.
- All automation services used can be monitored and continuously improved (AI Operations). General automation of workflows (Business Process Automation) through the Scheer PAS process execution engine.
Scheer PAS solution approach for process automation
Scheer PAS enables any form of automation, from routines that must be executed repeatedly by a classically developed program to more complex decision support using artificial intelligence. Integration makes it possible to provide the right data in the right system at any time and thus either increase the degree of automation (semi-automated processes) or automate complete business processes holistically.
With Scheer PAS Integration, more complex decision-making processes can be automated by "decision intelligence" and the provision of the required data directly in one step. Complex decisions, which are predominantly based on the consolidation of various information from different data sources, are thus automated directly in the process.
The following graphic shows an example process for automated invoice receipt processing:
Used Terms
The ability of machines to perform tasks that would normally require human intelligence, such as speech recognition, decision making, and learning from experience. AI technologies rely on complex algorithms and machine learning to analyze data, recognize patterns, and make predictions or recommendations.
Automation is the use of technology to perform tasks or processes that would otherwise be done manually by humans. Automation can involve the use of software, robots, or other types of machines to complete tasks with minimal human intervention.
Continuous Improvement is an ongoing process of enhancing products, services, processes, or systems to optimize their efficiency and effectiveness. It involves continuously identifying areas for improvement, analyzing them and implementing solutions to achieve better results.
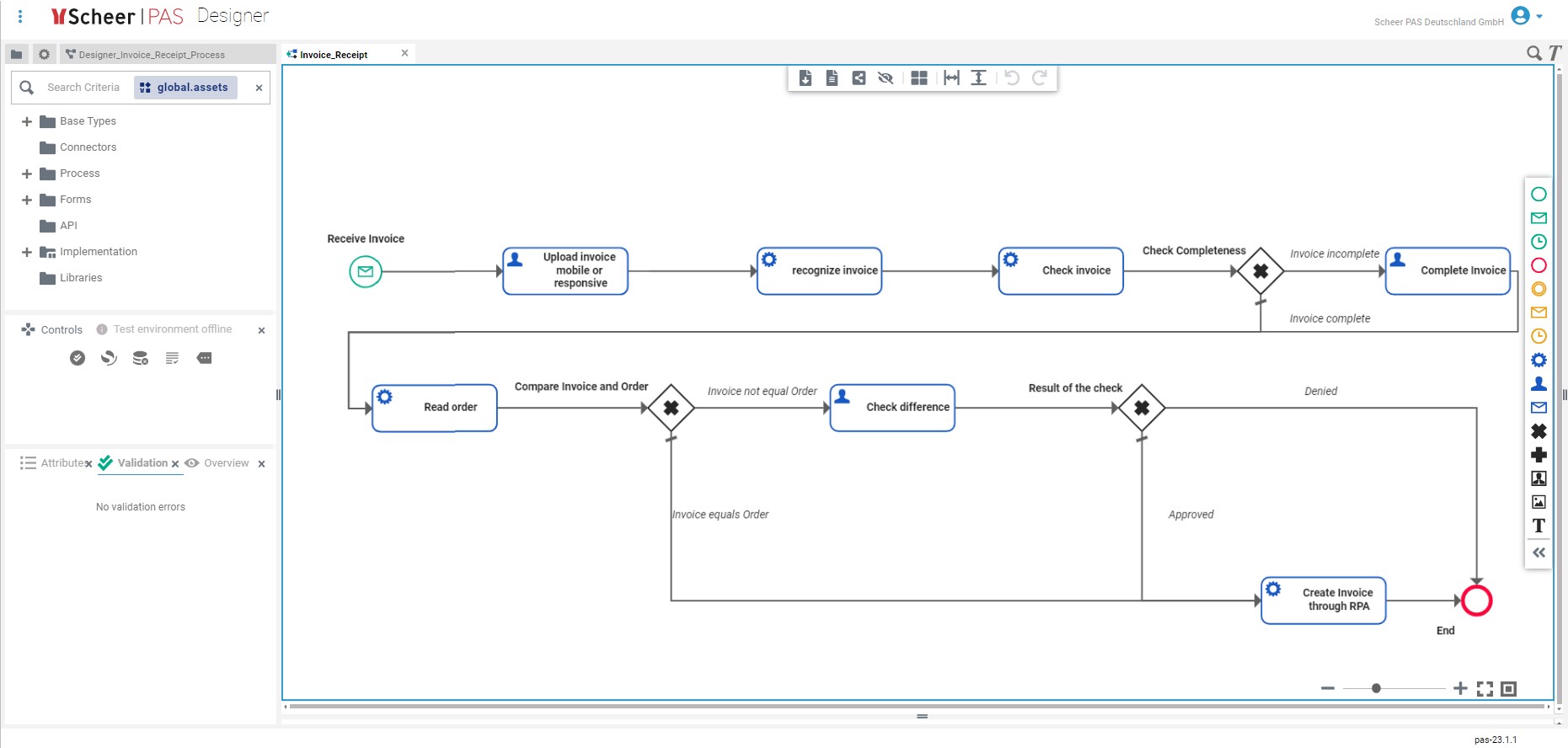
In this process, information is automatically extracted from invoice documents and the invoice items are automatically matched with the order data. In an intermediate manual step, the extracted data is validated once again and then automatically forwarded to a software robot.
Glossary of Process Automation Terms
Business rules are a set of guidelines and constraints that dictate how an organization operates. These rules define how various business processes should be executed, what decisions should be made in certain situations, and what actions should be taken to achieve certain results. Business rules can be used to ensure consistency, compliance, and efficient decision making.
Intelligent document processing (IDP) refers to the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies to extract information from unstructured documents such as invoices, contracts, and forms. IDP solutions typically use a combination of optical character recognition (OCR), natural language processing (NLP), and machine learning algorithms to scan, classify, and extract relevant data from documents.
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that enables machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning algorithms use statistical techniques to identify patterns and relationships within data and use these insights to make predictions or take action.
Smart services refer to online services that use advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT) to provide personalized, contextual, and proactive services to users.
Cognitive automation is a type of automation that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies to simulate human thought processes, such as perception, reasoning, and decision-making.
CRM is a strategy and approach used by organizations to manage and analyze their interactions and relationships with customers and potential customers. CRM systems typically store customer data and interactions across multiple channels, such as email, phone, social media, and website, and provide insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs.
Database administration is the management and maintenance of database systems to ensure their reliability, security and performance. This includes tasks such as database design, installation, configuration, backup and recovery, user administration, performance optimization, and security management.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of computer science and artificial intelligence that deals with enabling machines to understand, interpret and generate human language. It involves the use of algorithms and models to process and analyze natural language data, such as text, speech, and images, to produce meaningful insights and patterns.
Software bots are computer programs that automate repetitive or routine tasks, such as data entry, data extraction, and data processing, among others. They mimic human actions and interact with software applications and systems using user interfaces, APIs, or other protocols.
It involves automating the flow of tasks and information between different systems, departments, and stakeholders in a business process.